Differences between Eastern Massage and Western Massage
Contents
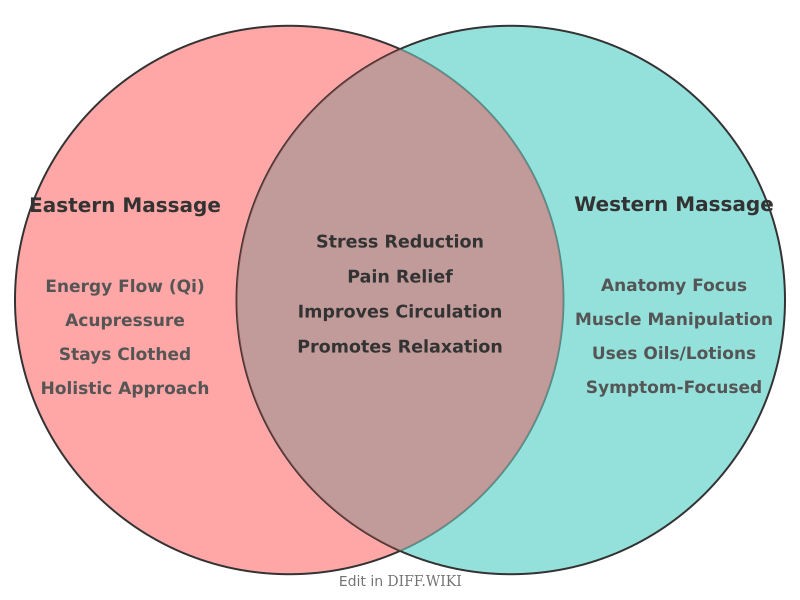
Differences between Eastern and Western Massage[edit]
Eastern and Western massage traditions are founded on different philosophical understandings of the body, health, and healing.[1] Eastern massage is rooted in traditional medicine systems like Traditional Chinese Medicine and Ayurveda, which view the body as a unified system of mind, body, and spirit.[1][2] In contrast, Western massage developed from a framework of modern anatomy and physiology, focusing on the body's physical structures such as muscles and joints.[3][4]
The primary goal of Eastern massage is to achieve balance and harmony within the body's energy systems.[3] Practitioners work to stimulate the flow of vital energy, known as *qi* or *prana*, along pathways called meridians.[3][5] Illness or pain is often seen as the result of blockages or imbalances in this energy flow. Western massage is typically more symptom-focused, aiming to alleviate specific physical issues like muscle tension, pain, and restricted movement by manipulating soft tissues.[3]
These differing philosophies lead to distinct therapeutic approaches. Eastern modalities often serve as a preventive practice to maintain overall well-being and are integrated with other practices like meditation and herbal medicine.[3] Western massage is frequently sought to address particular problems, with an emphasis on measurable outcomes such as an improved range of motion.[3]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Eastern Massage | Western Massage |
|---|---|---|
| Underlying Philosophy | Holistic; based on balancing the body's vital energy (*qi* or *prana*) along meridians.[3][5] | Mechanistic; based on anatomy and physiology.[3][4] |
| Primary Goal | Restore energy balance, promote holistic well-being, and maintain health.[3] | Relieve specific physical symptoms like muscle pain and tension, and improve circulation.[3] |
| Focus Area | Energy pathways (meridians) and pressure points throughout the body.[2] | Specific muscles, tendons, joints, and connective tissues.[3] |
| Therapeutic Approach | Addresses the whole person (body, mind, and spirit) to treat underlying energy imbalances.[1][2] | Targets the direct source of physical pain and discomfort.[1][2] |
| Common Techniques | Acupressure, stretching, rocking, and kneading to unblock energy flow.[2] | Long strokes (effleurage), kneading (petrissage), friction, tapping, and vibration. |
| Client Experience | Often performed on a floor mat with the client clothed; can be vigorous.[1] | Typically performed on a massage table with the client unclothed (draped); pressure can vary from gentle to deep. |
| Example Modalities | Shiatsu, Thai massage, Tui Na.[2] | Swedish massage, Deep Tissue massage, Sports massage.[3] |
Eastern Modalities: An Example[edit]
Shiatsu is a Japanese form of massage that translates to "finger pressure." Practitioners use thumbs, fingers, and palms to apply sustained pressure to specific points along the body's meridians. The core principle of shiatsu is to release blockages and stimulate the flow of *ki* (the Japanese term for *qi*) to restore the body's natural self-healing abilities. A session typically involves rhythmic and systematic pressure application, as well as gentle stretching, with the client remaining fully clothed.
Western Modalities: An Example[edit]
Swedish massage is one of the most widely known forms of Western massage. Its development is attributed to Per Henrik Ling in the early 19th century and is based on principles of anatomy and physiology. The primary goal is to promote relaxation by releasing muscle tension. Therapists use massage oils and employ five basic strokes: long, gliding strokes (effleurage); kneading and lifting of muscles (petrissage); deep, circular movements (friction); rhythmic tapping (tapotement); and shaking or vibrating movements. These techniques are designed to warm up muscle tissue, release tension, and break up muscle "knots."
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "keturah.com.au". Retrieved December 27, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "healthylife.com.au". Retrieved December 27, 2025.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 "neoni.co.nz". Retrieved December 27, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "massagebymarjie.com". Retrieved December 27, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "highstone.us". Retrieved December 27, 2025.