Differences between Emperor and King
Emperor vs. King[edit]
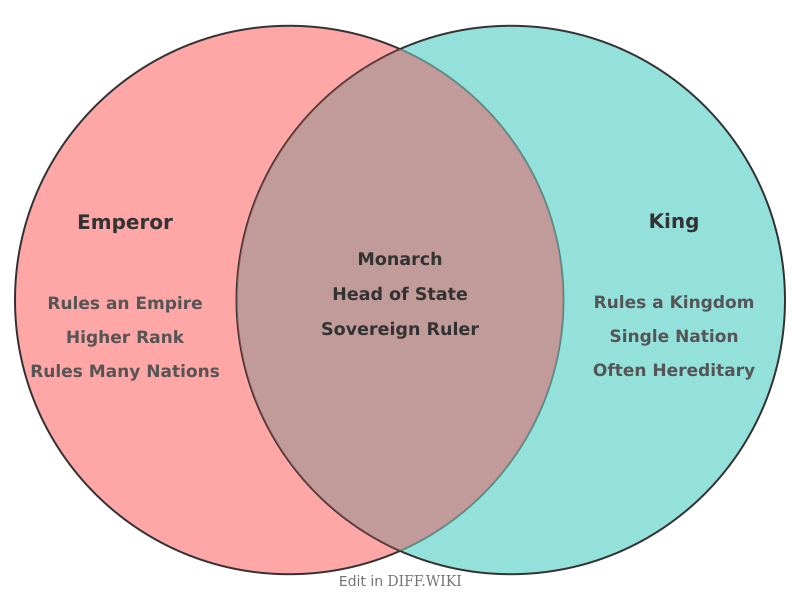
An emperor and a king are both monarchs, but the titles are not interchangeable. Historically, an emperor is considered a higher rank than a king.[1] The primary distinction lies in the scope and nature of their rule; an emperor governs an empire, which is typically a large territory composed of multiple nations or kingdoms, whereas a king rules over a single kingdom.[2][3]
The term "emperor" originates from the Latin word *imperator*, which in the Roman Republic referred to a victorious general.[4][5] It was later adopted as a title by the rulers of the Roman Empire, implying a commander with supreme military and political authority.[4] Consequently, the title often has connotations of a state built on conquest. In contrast, the word "king" is derived from the Old English *cyning*, meaning "son of the kin" or "descendant of noble birth," which points to a hereditary nature of succession within a specific ethnic or territorial group.
An emperor's authority, in theory, is supreme and not subject to any other secular ruler.[1] In some historical contexts, kings have been subordinate to an emperor, ruling their own kingdoms while owing allegiance to the higher monarch.[2] For example, some kings were vassals to the Holy Roman Emperor. The domain of an emperor, an empire, is often characterized by its vast size and ethnic and cultural diversity. A kingdom is generally smaller and more culturally homogeneous.
Succession practices have also varied. While kingship is almost universally hereditary, often following a system of primogeniture, imperial succession has historically been more varied. In the Roman Empire, for instance, succession was not strictly hereditary and could be determined by military might, adoption, or election by the Senate. In the Holy Roman Empire, emperors were elected by a group of prince-electors, although the position often remained within the same dynasty for long periods.[1]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Emperor | King |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of Rule | Typically rules over an empire, a collection of multiple states, nations, or diverse ethnic groups.[2] | Rules over a single kingdom or a more culturally homogenous territory. |
| Etymology | From the Latin *imperator*, meaning "commander." | From the Old English *cyning*, related to "kin" or noble birth. |
| Hierarchical Rank | Considered the highest monarchical rank, often holding sovereignty over kings.[1] | A sovereign ruler, but may be subordinate to an emperor in an imperial system.[2] |
| Basis of Authority | Often originally established through military conquest and supreme command (*imperium*). | Traditionally based on hereditary right and connection to a specific people or land. |
| Territorial Domain | Governs a large, often multi-ethnic and geographically expansive empire. | Governs a smaller, defined territory known as a kingdom. |
| Historical Succession | Varied; could be hereditary, elective (e.g., Holy Roman Empire), or through military power (e.g., Roman Empire).[1] | Primarily hereditary, typically passed down through a family line. |
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved October 17, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "sockgeeks.co.uk". Retrieved October 17, 2025.
- ↑ "study.com". Retrieved October 17, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "britannica.com". Retrieved October 17, 2025.
- ↑ "etymonline.com". Retrieved October 17, 2025.