Differences between FAT32 and NTFS
Contents
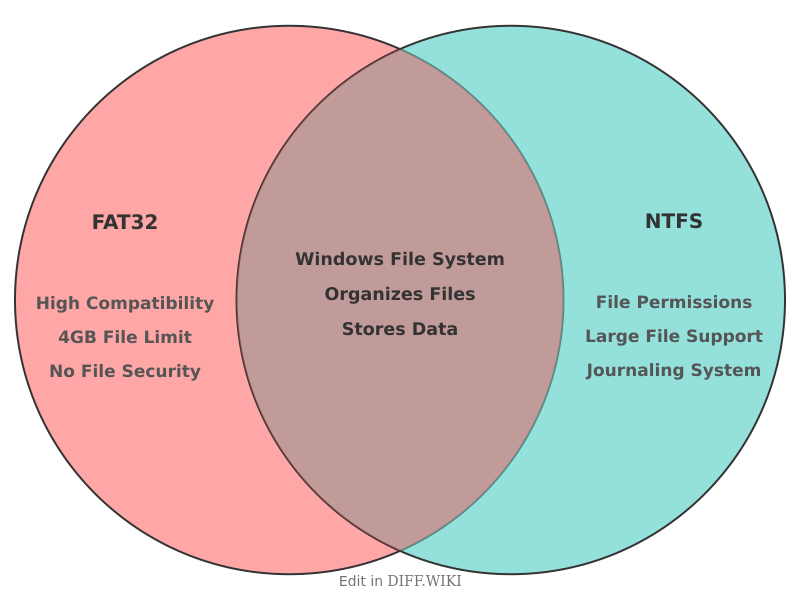
FAT32 vs. NTFS[edit]
Two common file systems developed by Microsoft are the File Allocation Table 32 (FAT32) and the New Technology File System (NTFS).[1][2] FAT32 was introduced with Windows 95 OSR2 and is an older file system, while NTFS was introduced with Windows NT in 1993 and is the default for most modern Windows operating systems.[3][4][5] The choice between them depends on the specific needs of the user, as each has distinct advantages and limitations regarding file and partition size, security, and operating system compatibility.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | FAT32 | NTFS |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum File Size | 4 GB[3] | 256 TB (on Windows 10 version 1709 and later) |
| Maximum Partition Size | 8 TB | 8 PB (on Windows 10 version 1709 and later) |
| Security | No file-level security or encryption | Supports file permissions, access control lists (ACLs), and encryption |
| Compression | No built-in compression | Supports individual file and folder compression |
| Fault Tolerance | No journaling capabilities | Journaling file system helps recover from errors |
| OS Compatibility | High compatibility with various operating systems including Windows, macOS, and Linux[3] | Primarily for Windows; macOS and some Linux distributions have read-only access without third-party software[5] |
Key Differences[edit]
File and Partition Size[edit]
A significant limitation of FAT32 is its inability to store individual files larger than 4 GB.[3] This makes it unsuitable for large files such as high-resolution videos or large databases. NTFS, on the other hand, supports much larger file sizes, up to 256 terabytes on recent Windows versions. Similarly, FAT32 has a maximum partition size of 8 TB, whereas NTFS can support partitions up to 8 petabytes.
Security and Compression[edit]
FAT32 offers minimal security features, lacking support for file permissions and encryption. This can leave data vulnerable to unauthorized access. In contrast, NTFS provides robust security options, including the ability to set specific permissions for files and folders for different users and to encrypt data through the Encrypting File System (EFS). NTFS also supports transparent file compression, which can help save disk space. FAT32 does not have a native compression feature.
Reliability and Compatibility[edit]
NTFS is a journaling file system, meaning it keeps a log of changes made to the files on the disk. This feature allows for quicker recovery from system crashes or power failures and helps prevent data corruption. FAT32 does not have this journaling capability.
However, FAT32 has broader compatibility across different operating systems. It is widely supported by Windows, macOS, and Linux, as well as many consumer devices like gaming consoles and cameras.[3] NTFS is the standard for Windows but has limited compatibility with other operating systems.[5] For example, macOS can read from NTFS drives but cannot write to them without additional software.
References[edit]
- ↑ "byjus.com". Retrieved January 06, 2026.
- ↑ "gorelo.io". Retrieved January 06, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "siberoloji.com". Retrieved January 06, 2026.
- ↑ "datto.com". Retrieved January 06, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "mettec.net". Retrieved January 06, 2026.