Differences between FDI and FPI
Contents
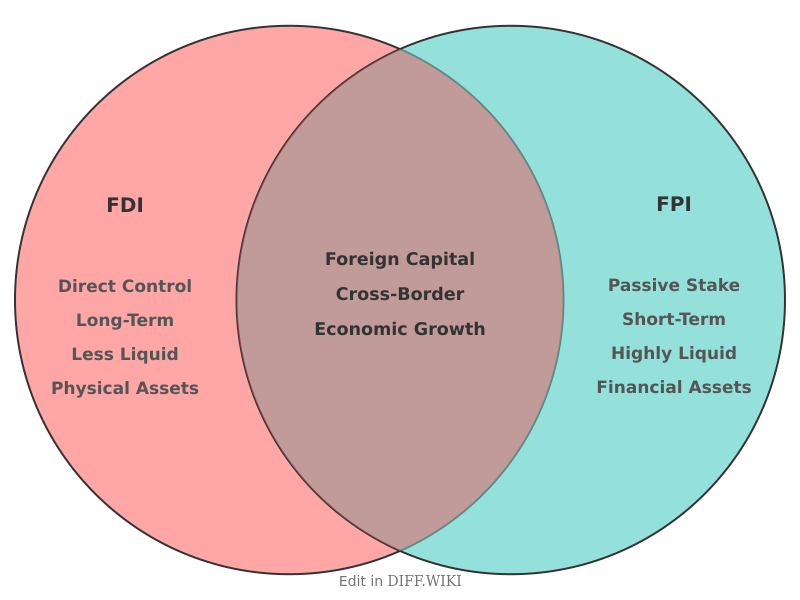
Foreign Direct Investment vs. Foreign Portfolio Investment[edit]
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) are two primary methods for investing capital in a foreign country.[1] FDI involves an investor establishing a direct business interest in a foreign country, which can include activities like building new facilities or acquiring a significant stake in an existing company.[2][3] In contrast, FPI refers to the purchase of financial assets, such as stocks and bonds, from a foreign country without direct management control over the company.[2] The fundamental distinction between the two lies in the level of control and the duration of the investment.[2]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) | Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) |
|---|---|---|
| Nature of Investment | Direct investment in physical assets, such as factories, machinery, and buildings.[4][5] | Indirect investment in financial assets like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.[5] |
| Investor Control | The investor gains significant influence or direct control over the foreign business's operations and management. | The investor's role is passive, with no direct control over the company's day-to-day operations.[1] |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term commitment, often spanning years or decades.[4] | Generally short-term in nature, with investors able to enter and exit the market quickly.[2] |
| Volatility and Stability | Considered more stable and less prone to sudden withdrawals during market fluctuations.[4] | More volatile and sensitive to market sentiment, sometimes referred to as "hot money" due to rapid inflows and outflows.[4][1] |
| Ease of Entry and Exit | Entry and exit are complex and time-consuming due to the illiquid nature of physical assets.[4] | Relatively easy to enter and exit, as financial assets are highly liquid and can be traded quickly.[4] |
| Economic Impact | Contributes directly to job creation, infrastructure development, and technology transfer in the host country.[1] | Primarily affects the liquidity of capital markets and has a less direct impact on broader economic development.[5] |
Investor's Role and Market Stability[edit]
The level of an investor's involvement is a primary differentiator between FDI and FPI. FDI investors are actively involved in the management of their investments, often taking controlling positions in domestic firms or through joint ventures.[5] This long-term perspective means FDI is less susceptible to market turbulence, as physical assets cannot be quickly liquidated.[3]
Conversely, FPI investors are passive and do not participate in the daily management of the companies they invest in.[5] Their focus is on financial returns from the securities market. The high liquidity of these assets allows for rapid buying and selling, which can lead to market volatility.[4][5] During periods of economic uncertainty, FPI can be withdrawn quickly, potentially causing economic instability in the host country.[1]
Impact on the Host Country's Economy[edit]
FDI is often viewed as a significant contributor to the sustainable economic development of the host country.[1] It goes beyond capital investment by bringing in new technologies, management skills, and creating jobs. The establishment of new facilities and infrastructure directly boosts economic activity.
FPI, while an important source of capital for financial markets, does not have the same direct impact on the broader economy.[5] It increases the liquidity of domestic capital markets but is not typically associated with the long-term development of industries or infrastructure. For this reason, FDI is often considered more favorable for a host nation's long-term growth.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "investopedia.com". Retrieved February 05, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "kuvera.in". Retrieved February 05, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "kotakneo.com". Retrieved February 05, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 "investopedia.com". Retrieved February 05, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 "cleartax.in". Retrieved February 05, 2026.