Differences between Felony and Misdemeanor
Comparison Article[edit]
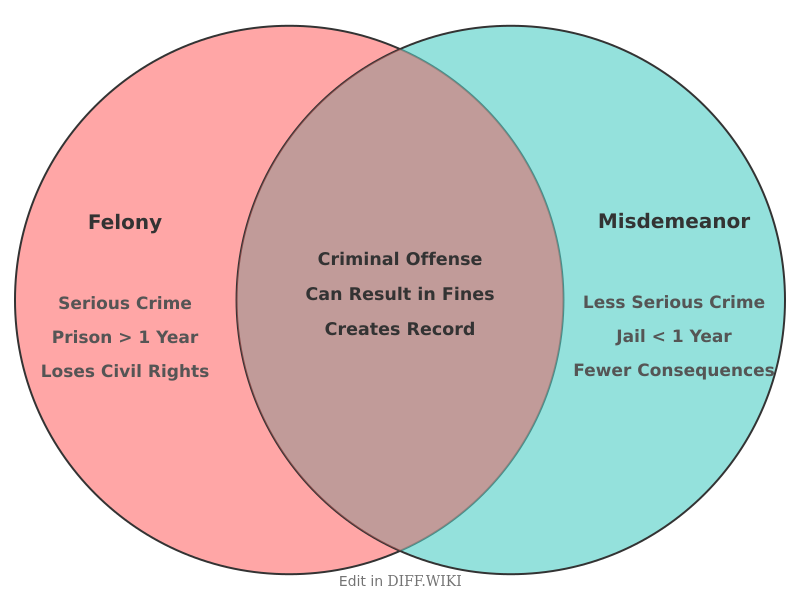
In the American legal system, crimes are generally categorized into two main classifications: felonies and misdemeanors.[1] The primary distinction between these categories lies in the seriousness of the offense, which in turn dictates the severity of the potential punishment.[2] Many states classify misdemeanors and felonies into different classes or degrees to further delineate the gravity of the crime and its corresponding penalties.[1]
A felony is a serious crime that carries a potential punishment of more than one year of incarceration.[3] These offenses often involve violence or significant harm to individuals or property.[4][1] Conversely, a misdemeanor is a less serious offense, typically punishable by up to one year in jail, fines, probation, or community service.[5] The classification of a crime as either a felony or a misdemeanor can vary by jurisdiction, with some offenses being classified differently from one state to another.[1] Certain crimes, sometimes referred to as "wobblers," can be charged as either a felony or a misdemeanor depending on the specifics of the case.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Felony | Misdemeanor |
|---|---|---|
| Examples of Offenses | Murder, robbery, burglary, aggravated assault, grand theft, and drug trafficking.[4] | Petty theft, simple assault, vandalism, disorderly conduct, and first-offense DUIs. |
| Potential Incarceration | More than one year in a state or federal prison.[5][3] In some cases, life imprisonment or the death penalty may be imposed.[4] | Up to one year in a local or county jail.[5][2] |
| Legal Process | Often involves a grand jury indictment and a more complex and lengthy court process. | Typically initiated by a complaint from a prosecutor, with a more streamlined legal process. |
| Long-Term Consequences | A felony conviction can result in the loss of civil liberties, such as the right to vote, own a firearm, or serve on a jury. It can also create significant barriers to employment and housing. | While less severe, a misdemeanor conviction creates a criminal record that can impact employment, housing, and professional licensing opportunities. |
| Record Expungement | Generally, a felony conviction remains on a person's criminal record for life and is rarely eligible for expungement. | Misdemeanor convictions may be eligible for expungement after a certain period, depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the crime. |
The legal process for felonies and misdemeanors also differs significantly. Felony cases often begin with an arrest and may involve a grand jury, which decides if there is enough evidence to issue an indictment and proceed to trial. Misdemeanor cases, on the other hand, are typically initiated when a prosecutor files a complaint, and the process is generally less complex.
The long-term impact of a felony conviction is substantially more severe than that of a misdemeanor. A person convicted of a felony, known as a felon, can lose certain civil rights, including the right to vote, hold public office, or possess a firearm. Finding employment and housing can also be challenging with a felony record. While a misdemeanor conviction is less impactful, it still results in a criminal record that can present obstacles in various aspects of life. In some instances, misdemeanor records can be expunged, or cleared, after a certain amount of time has passed, an option that is seldom available for felony convictions.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "grabellaw.com". Retrieved February 09, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "bhattchicagodefenselaw.com". Retrieved February 09, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "justia.com". Retrieved February 09, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "nycriminaldefenders.com". Retrieved February 09, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "samson-law.com". Retrieved February 09, 2026.