Differences between Fog and Mist
Fog vs. Mist[edit]
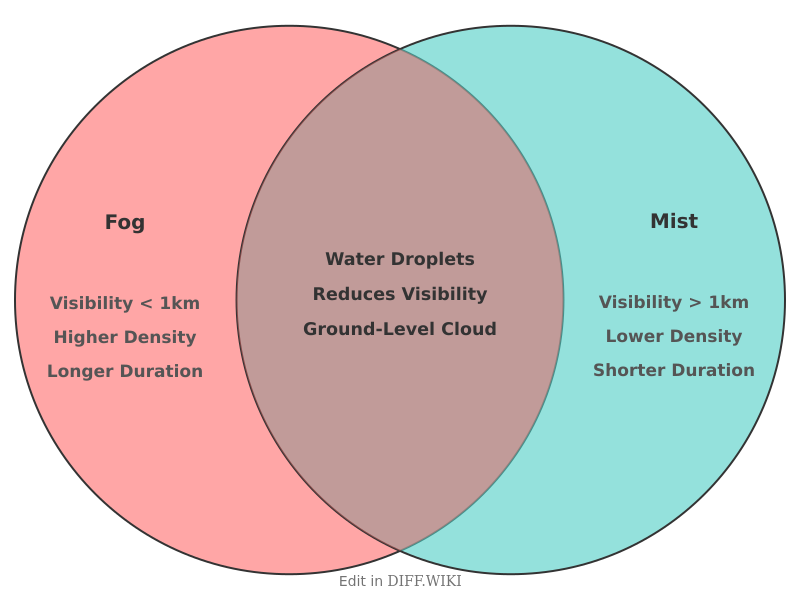
Fog and mist are both atmospheric phenomena consisting of suspended water droplets that reduce visibility at or near the Earth's surface.[1] They are essentially clouds that form at ground level when water vapor condenses.[2] The primary distinction between the two is based on the density of the water droplets, which directly impacts the degree of visibility reduction.[3]
By international meteorological definition, the key difference is a specific visibility threshold.[1] An atmospheric obscurity is classified as fog if the horizontal visibility is less than 1 kilometer (approximately 5/8 of a mile).[4] If the visibility is 1 kilometer or greater, it is referred to as mist.[3] Fog is denser and thicker than mist, appearing as a whitish veil that can significantly obscure the landscape, while mist is less dense and typically forms a thinner, greyish veil.[4][1]
The formation of both fog and mist occurs when air becomes saturated with water vapor, either through cooling to its dew point or by the addition of moisture.[5] This causes the water vapor to condense around microscopic airborne particles, such as dust or salt, known as condensation nuclei. The conditions for formation are similar, though fog generally requires a higher concentration of condensed water droplets to achieve its lower visibility.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Fog | Mist |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Less than 1 kilometer (0.62 miles).[4] | 1 kilometer or more.[3] |
| Density | Higher density of water droplets, appears more opaque.[1] | Lower density of water droplets, appears more translucent.[3] |
| Appearance | A thick, whitish veil that can obscure landscapes.[4] | A thin, greyish veil.[4] |
| Relative Humidity | Typically forms when relative humidity is between 95% and 100%.[1][5] | Forms when relative humidity is high, generally above 95%.[1] |
| Droplet Size | Droplet sizes can vary, but are generally smaller than 100 microns (0.1mm) in diameter.[5] | Droplets are also small, with some sources indicating sizes between 30 and 60 microns. |
| Dissipation | Tends to be more persistent and takes longer to dissipate.[1] | Can dissipate more rapidly, especially with light wind.[3] |
Composition and Feel[edit]
Both fog and mist are composed of tiny liquid water droplets suspended in the air.[1] The air within fog often feels damp or wet to an observer.[4] While the core composition is the same, the concentration of these droplets is what creates the difference in visual density and opacity. Due to its higher density, fog is more effective at scattering light, which is why it appears thicker and reduces visibility more significantly than mist.[5]
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 "wisc.edu". Retrieved December 24, 2025.
- ↑ "medium.com". Retrieved December 24, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "metoffice.gov.uk". Retrieved December 24, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 "wmo.int". Retrieved December 24, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "metoffice.gov.uk". Retrieved December 24, 2025.