Differences between Kindle and Nook
Contents
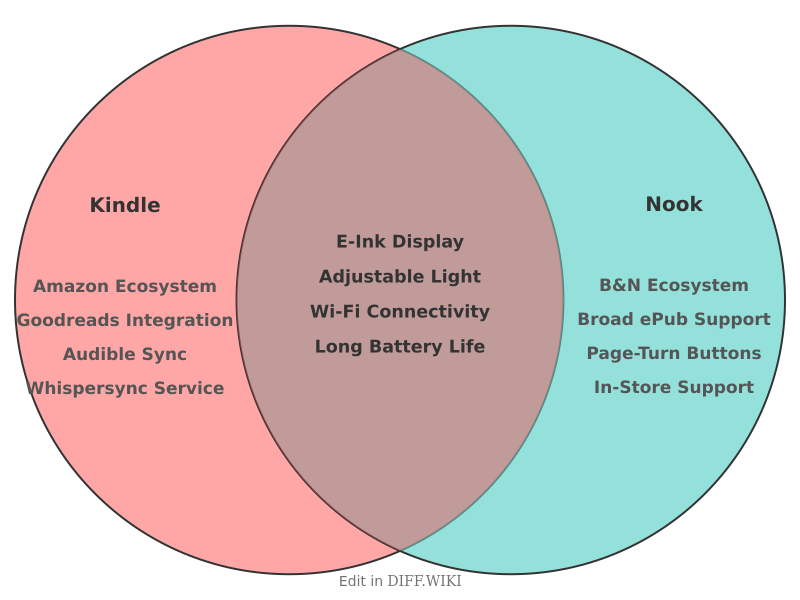
Kindle vs. Nook[edit]
The Amazon Kindle and Barnes & Noble Nook are two of the most prominent brands of e-readers.[1] Both device lines offer models with E Ink screens designed to mimic the appearance of paper, providing a different reading experience from tablets with LCD screens.[2][3] While both serve the primary function of displaying digital books, they differ in their hardware design, software features, and the ecosystems of content they support.[4]
Amazon released the first Kindle in 2007, which was instrumental in shaping the digital reading market.[5] Barnes & Noble, a major book retailer in the United States, introduced its first Nook e-reader in 2009. Over the years, both companies have released numerous generations and models of their respective devices, including e-readers with integrated lights, higher-resolution displays, and color tablet versions.[5][3]
The primary distinction between the two lines lies in their content stores and file format compatibility.[1] Kindle devices are integrated with the Amazon Kindle Store, which has a larger catalog of titles, including a significant number of self-published and exclusive books. Nook devices connect to the Barnes & Noble Nook Store. A key technical difference is Nook's native support for the EPUB file format, a common standard used by public libraries, whereas Kindle primarily uses its own proprietary formats like AZW3.[4]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Kindle | Nook |
|---|---|---|
| Parent Company | Amazon | Barnes & Noble |
| Ebook Store | Amazon Kindle Store[2] | Barnes & Noble Nook Store[2] |
| Library Size | Larger selection, estimated at over 12 million titles, with many indie and exclusive works | Smaller selection, estimated around 4 million titles, with a focus on major publishers |
| Native File Format | AZW3, AZW | EPUB, PDF |
| Library Book Borrowing (Libby) | Direct, wireless integration once accounts are linked | Manual transfer required via a computer using Adobe Digital Editions[4] |
| Physical Page-Turn Buttons | Available only on the older Kindle Oasis model | Included on all Nook GlowLight e-reader models |
| Subscription Service | Offers Kindle Unlimited and Amazon Prime Reading for access to a rotating catalog of ebooks[2] | Does not offer an ebook subscription service comparable to Kindle Unlimited[5] |
| Waterproofing | Available on models such as the Paperwhite and Oasis | Available on higher-end models like the Nook GlowLight 4 Plus |
| Audiobook Support | All current models support Audible audiobooks via Bluetooth | Support is limited to specific models like the GlowLight 4 Plus via Bluetooth or headphone jack |
Hardware and Design[edit]
Kindle and Nook e-readers are available in various models at competitive price points.[2] Generally, Kindle hardware is considered to have a more premium feel, with some models featuring a flush-front screen design. Nook's e-ink devices are notable for including physical page-turn buttons on the sides of the bezel, a feature preferred by some users for providing a more tactile reading experience.[5] Most Kindle models rely solely on a touchscreen for page navigation.
Screen sizes and resolutions are largely comparable between competing models, with both brands offering devices with 300 ppi E Ink displays that are glare-free. Storage capacity is also similar, with entry-level models from both brands typically offering sufficient space for thousands of ebooks.
Software and Ecosystem[edit]
The user experience on Kindle and Nook devices is shaped by their respective software and integration with their parent company's services. The Kindle ecosystem is deeply integrated with Amazon's other offerings, including Audible for audiobooks and Goodreads for book recommendations and reviews. Kindle's software includes features like X-Ray, which allows readers to look up information about characters and terms within a book, and Word Wise, which provides simple definitions for difficult words.
The Nook's software is often described as offering a more straightforward and focused reading experience. While it lacks some of Kindle's extra features, it provides customization options for fonts and page layout. A significant advantage of the Nook ecosystem is the in-person support available at Barnes & Noble retail stores.[5][4]
For borrowing ebooks from public libraries, the Kindle offers a more streamlined process through its integration with Libby (formerly OverDrive). Users can send library books directly to their Kindle from the library's website or the Libby app. Nook users must typically use a computer to download the library ebook and manually transfer it to their device.[4]
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "difference.wiki". Retrieved January 06, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "bestbuy.com". Retrieved January 06, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "the-ebook-reader.com". Retrieved January 06, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "slashgear.com". Retrieved January 06, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved January 06, 2026.