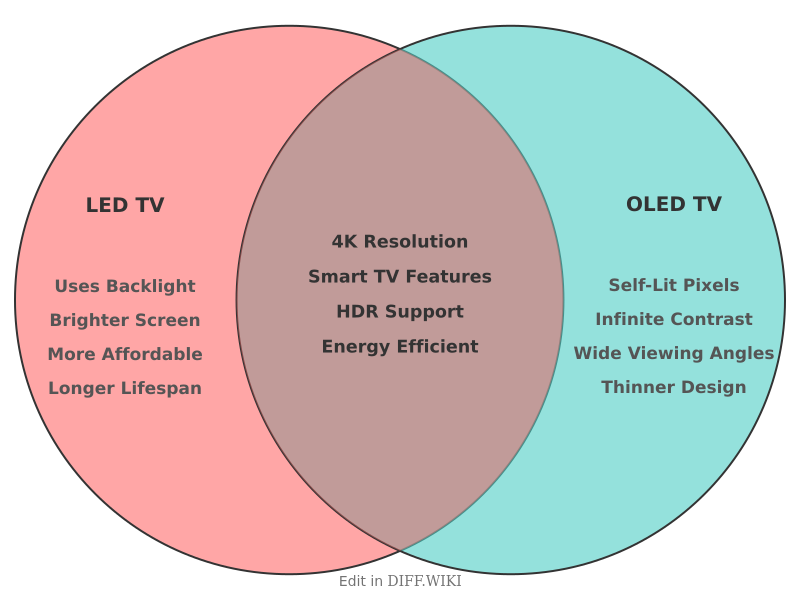
Differences between LED TV and OLED TV
LED TV vs. OLED TV[edit]
Light-emitting diode (LED) and organic light-emitting diode (OLED) are two distinct television display technologies.[1] An LED TV is a type of liquid crystal display (LCD) that uses a backlight made of LEDs to illuminate the screen.[2][3] In contrast, OLED TVs utilize organic compounds that emit their own light when an electric current is applied, a process known as electroluminescence.[4][1] This fundamental difference in how they produce light results in varied performance in picture quality, design, and other aspects.[5]
LED TVs are a more established and widely available technology, offered in a broad range of sizes and price points. OLED technology is newer and generally positioned in the premium market segment.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | LED TV | OLED TV |
|---|---|---|
| Backlight | Uses a separate LED backlight to illuminate a liquid crystal panel.[5] | Each pixel produces its own light (self-emissive); no backlight is needed.[5] |
| Black Levels & Contrast | Black levels are limited by the backlight, which can result in a lower contrast ratio.[3] | Can achieve true black by turning individual pixels completely off, resulting in a theoretically infinite contrast ratio.[4] |
| Brightness | Generally capable of higher peak brightness levels, making them suitable for well-lit rooms.[1] | Typically has lower overall brightness compared to high-end LED models.[3] |
| Viewing Angle | Picture quality, including color and contrast, can degrade when viewed from wider angles. | Maintains consistent color and contrast from wide viewing angles.[4] |
| Response Time | Has a slower response time, which can sometimes result in motion blur. | Possesses a faster response time, leading to smoother motion for content like sports and video games.[1] |
| Power Consumption | Generally more energy-efficient, particularly at high brightness levels.[3] | Power consumption varies with screen content; displaying bright images uses more power. |
| Lifespan & Burn-in | Has a longer lifespan and is less susceptible to burn-in.[1] | The organic materials can degrade over time, and the display is more prone to permanent image retention, or burn-in, with static images. |
| Design | The need for a separate backlight results in a thicker and heavier television. | The absence of a backlight allows for an exceptionally thin and lightweight design. |
Image Quality[edit]
The primary distinction in image quality stems from how each technology handles darkness. Because OLED pixels can be turned off individually, they can produce absolute black, which enhances the perceived contrast and makes colors appear more vibrant. LED TVs rely on dimming the backlight in dark areas of the image, but some light leakage is common, preventing the display from achieving the same level of black.
While high-end LED TVs can produce a brighter overall image, which is advantageous in brightly lit environments, OLED TVs are often favored for their superior contrast and color accuracy in controlled lighting conditions.[3][1]
Longevity[edit]
LED technology is considered more durable and has a longer lifespan compared to OLED. The organic compounds in OLED displays degrade over time, which can lead to a decrease in brightness and shifts in color balance.[1] OLED screens are also more susceptible to "burn-in," a phenomenon where a static image displayed for a prolonged period can leave a permanent ghost-like artifact on the screen. Manufacturers have implemented technologies like pixel shifting to mitigate this issue, and for typical mixed use, it is less of a concern.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "ossila.com". Retrieved January 13, 2026.
- ↑ "spencerstv.com". Retrieved January 13, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "philips.co.uk". Retrieved January 13, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "samsung.com". Retrieved January 13, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "crutchfield.com". Retrieved January 13, 2026.