Differences between Laptop and Netbook
Contents
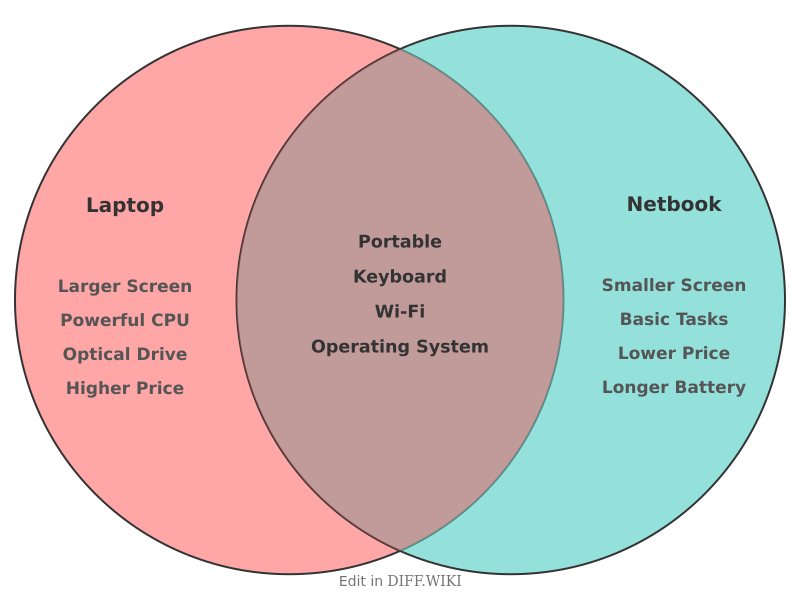
Laptop vs. Netbook[edit]
A laptop is a portable personal computer with a hinged clamshell form factor, suitable for a variety of tasks.[1] A netbook is a now-largely defunct category of laptop that was smaller, lighter, and less expensive than typical notebooks.[2][3] Netbooks emerged in the late 2000s, designed primarily for internet access and basic productivity tasks.[4][1] The term "netbook" was popularized by Intel in 2008 to market its low-power Atom processors, which were common in these devices.[4][5]
Laptops, also referred to as notebooks, function as replacements for desktop computers, offering comparable performance for a wide range of applications.[1] Netbooks, in contrast, were not intended to be a user's primary computer. They offered limited processing power and were best suited for web browsing, email, and word processing.[1] Their low cost and portability were their main selling points.[2]
The popularity of netbooks declined by the early 2010s.[2] Factors contributing to their demise included the increasing affordability of more powerful, full-sized laptops, and the rise of tablet computers and smartphones, which fulfilled the need for a highly portable internet device.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Laptop | Netbook |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | General computing, content creation, gaming[3] | Web browsing, email, basic productivity[1] |
| Screen Size | Typically 13 to 17 inches or larger[1] | Generally 7 to 12 inches[2] |
| Processing Power | More powerful processors (e.g., Intel Core, AMD Ryzen) | Low-power processors (e.g., Intel Atom)[2] |
| Storage | Larger capacity hard drives (HDD) or solid-state drives (SSD) | Smaller capacity SSDs or HDDs[2] |
| Weight | Generally heavier, from 3 lbs (1.4 kg) upwards[1] | Lighter, typically 2-3 lbs (around 1 kg)[2] |
| Cost | Higher, wide price range based on specifications[1] | Lower, positioned as a budget-friendly option[4] |
| Optical Drive | Often included in older models; less common now | Almost never included[2] |
Performance and Use Cases[edit]
Laptops are designed to be versatile computing devices. Their more powerful processors, greater amounts of RAM, and superior graphics capabilities allow them to handle demanding tasks such as video editing, graphic design, and modern gaming.[3] The larger screens and full-sized keyboards provide a more comfortable user experience for extended periods of work or entertainment.[1]
Netbooks were created for a different purpose. They focused on portability and affordability, which necessitated compromises in performance. Equipped with energy-efficient processors like the Intel Atom, they provided enough power for basic internet-related activities but struggled with multitasking or resource-intensive software. Their smaller size also meant smaller, more cramped keyboards and lower-resolution displays.[2] Early models often used Linux-based operating systems to reduce costs and system requirements, though later versions commonly ran starter editions of Microsoft Windows.[4]
Market Decline[edit]
The market for netbooks was short-lived. Initially popular after the launch of models like the Asus Eee PC in 2007, sales began to decline sharply by 2011.[2] Several factors led to this. As manufacturing costs decreased, the price gap between netbooks and more capable budget laptops narrowed. Consumers who purchased netbooks expecting performance comparable to a traditional laptop were often disappointed by their limitations.
The most significant challenge to the netbook market came from new device categories. The introduction of Apple's iPad in 2010 offered a user-friendly, highly portable device for media consumption and web browsing, a key use case for netbooks. Concurrently, the growing capabilities of smartphones also reduced the need for a separate, small computing device for internet access on the go. By the end of 2012, most major manufacturers had ceased producing netbooks.[2] The legacy of the netbook can be seen in the development of other low-cost, web-focused laptops like the Chromebook.[4]
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "geeksforgeeks.org". Retrieved December 08, 2025.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved December 08, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "lenovo.com". Retrieved December 08, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "britannica.com". Retrieved December 08, 2025.
- ↑ "kiddle.co". Retrieved December 08, 2025.