Differences between Mouse and Rat
Contents
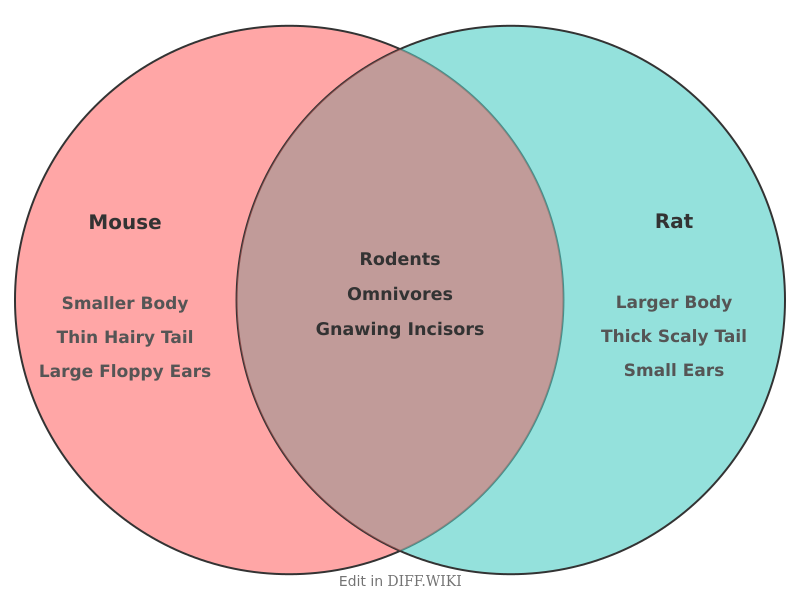
Mouse vs. Rat[edit]
Though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, mice and rats are distinct types of rodents.[1] Both belong to the Muridae family, but they are classified under different genera.[2] The common house mouse is in the genus Mus, while the Norway rat and black rat belong to the genus Rattus.[2][3] Rats are generally larger and heavier than mice.[4] A young rat can be mistaken for an adult mouse, but juvenile rats have disproportionately large heads and feet compared to their bodies.[4]
Comparison table[edit]
| Category | Mouse | Rat |
|---|---|---|
| Body Size | Small, typically 3-4 inches (8-10 cm) long, excluding the tail.[5] | Large, typically 7-11 inches (18-28 cm) long, excluding the tail. |
| Weight | ½ to 1 ounce (14-28 grams). | Up to 1 pound (450 grams). |
| Snout Shape | Triangular and pointed. | Blunt and more rounded or wedge-shaped. |
| Ears | Large in proportion to the head. [1] | Small in proportion to the head. |
| Tail | Thin, sometimes lightly haired, and typically as long as or longer than the body. | Thick, hairless, and scaly; usually shorter than the body. |
| Diet | Prefers cereals, seeds, and fruit; nibbles on many different food items. | Omnivorous, eating almost anything, including meat and garbage; tends to eat large quantities from one source. |
| Behavior | Generally curious and will investigate new objects in its path. | Cautious and often avoids new objects (neophobic). |
| Lifespan | Around 9 to 12 months in the wild. | Approximately one year in the wild. |
Physical characteristics[edit]
The most apparent difference between mice and rats is their size. Adult[5] rats are significantly larger and heavier than adult mice. Their[4] body shapes also differ; mice have small, slender bodies, while rats are bulkier and more robust. [5] Head shape is another distinguishing feature. A mouse has a small, triangular head with a pointed snout and proportionally large ears and eyes. A rat has a broader, more blunt head with ears and eyes that are small relative to its head size.
Their tails are also distinct. A mouse's tail is thin and can be covered in a fine layer of hair, often measuring about the same length as its body. In contrast, a rat's tail is thick, hairless, and features visible scaly rings. [1]
Behavior and habitat[edit]
Mice and rats exhibit different behaviors, particularly in how they react to new situations. Mice are often described as curious and will typically explore new items they encounter. Rats, however, are neophobic, meaning they are wary of new objects and changes in their environment, which can make them more difficult to trap.
Their nesting and habitat preferences also vary. Mice prefer to build nests in hidden areas close to a food source, such as inside walls, cabinets, or storage boxes, using soft materials. Some rat species, like the Norway rat, are burrowers that create nests underground or in lower levels of buildings, such as basements. Other species, like the roof rat, are skilled climbers and prefer elevated nesting spots in attics or trees.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "dictionary.com". Retrieved December 31, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "reddit.com". Retrieved December 31, 2025.
- ↑ "wikipedia.org". Retrieved December 31, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "rentokil.co.uk". Retrieved December 31, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "nativepestmanagement.com". Retrieved December 31, 2025.