Differences between Neolithic and Paleolithic
Contents
Paleolithic vs. Neolithic[edit]
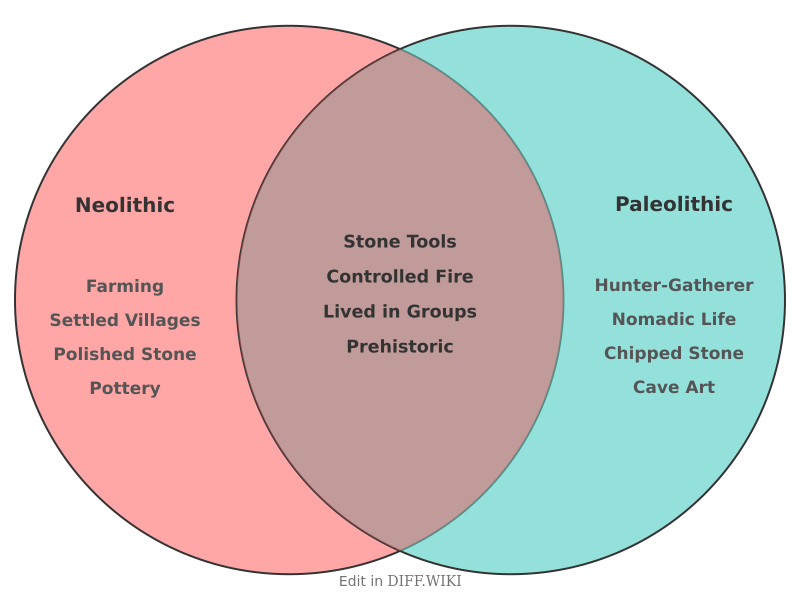
The Paleolithic and Neolithic periods are the two earliest eras of the Stone Age. The Paleolithic, or Old Stone Age, was a long period of early human development characterized by a nomadic, hunter-gatherer lifestyle.[1][2] The Neolithic, or New Stone Age, was a shorter period that saw the advent of agriculture, leading to settled communities.[3][4] This transition from food collection to food production marked a significant turning point in human history.[1]
The shift between these two eras occurred at different times in different parts of the world, generally beginning around 10,000 BCE in the Near East.[5][2] The development of agriculture in the Neolithic period led to widespread changes in society, including increased population, the emergence of permanent villages, and the development of new technologies.[4] While Paleolithic people used chipped stone tools, Neolithic tools were often more sophisticated and polished.[5]
Comparison Table[edit]
[1]| Lifestyle| Category | Paleolithic | Neolithic |
|---|---|---|
| Time Frame | c. 2.5 million years ago – 10,000 BCE | [1] c. 10,000 BCE – 2,000 BCE |
| Food Source | Hunting, fishing, and gathering wild plants | Cultivated[2] crops (like wheat and barley) and domesticated animals (like cattle, sheep, and goats) |
| Nomadic, living in small bands of 25-50 people | Sedentary, living in permanent settlements and villages | |
| Dwellings | Temporary shelters like caves, huts, and tents made of animal skins | Permanent structures made of mud brick and timber |
| Tools | Chipped stone tools, as well as tools made of bone and wood | Polished stone tools, sickle blades, grinding stones, and pottery |
| Social Structure | Small tribal societies or clans, generally egalitarian | More hierarchical societies with the emergence of leaders and social classes |
| Art | Cave paintings, small sculptures of animal and human forms ("Venus figurines") | Wall paintings, pottery, larger sculptures, and megalithic architecture (e.g., Stonehenge) |
Social and Economic Differences[edit]
Paleolithic societies were organized into small, nomadic bands. The economy was based on hunting and gathering, and there was likely no concept of private property. Social[2] structures were generally egalitarian, with leadership often based on age or skill.
The Neolithic Revolution brought about significant changes. The development of agriculture allowed for a more stable food supply, which in turn supported larger, settled populations. This[4] led to the formation of villages and, eventually, more complex social structures. With permanent settlement came the concept of land ownership and a greater accumulation of personal possessions. Evidence from Neolithic burial sites, where some individuals were interred with valuable objects like pottery and jade, suggests the emergence of social hierarchies and classes.
Art and Technology[edit]
The primary technological distinction between the two eras lies in the production of stone tools. Paleolithic tools were typically created by chipping stones to create an edge. Neolithic toolmakers, by contrast, learned to grind and polish stones, resulting in sharper and more durable implements. The Neolithic also saw the invention of pottery for food storage and cooking, as well as the development of weaving and other crafts.
Art also evolved significantly between the two periods. Paleolithic art is known for its naturalistic cave paintings of animals and small, portable sculptures. As people began to live in permanent settlements, new art forms emerged. Neolithic art includes more depictions of human figures and daily life. The construction of permanent dwellings led to the development of architecture and wall paintings. This period is also known for its megalithic structures, such as Stonehenge, which would have required significant community effort to construct.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "studentsofhistory.com". Retrieved November 05, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "pressbooks.pub". Retrieved November 05, 2025.
- ↑ "pediaa.com". Retrieved November 05, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "superioressaywriters.com". Retrieved November 05, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "britannica.com". Retrieved November 05, 2025.