Differences between Obesity and Overweight
Contents
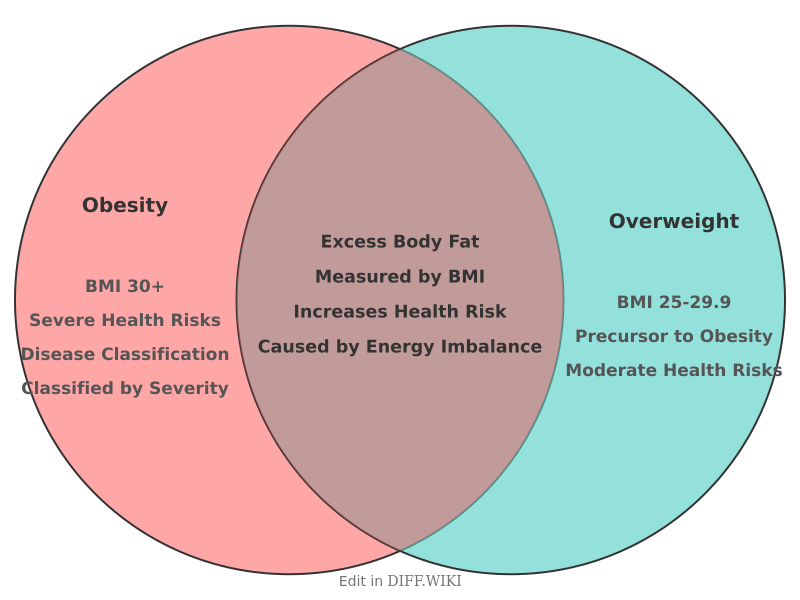
Differences between Obesity and Overweight[edit]
Overweight and obesity are both terms for excess body fat accumulation that can pose health risks.[1][2] The primary distinction between the two is the degree of excess fat.[3]
Body Mass Index (BMI) is the most common tool used to determine if an individual is overweight or obese.[4][5] It is a calculation based on a person's height and weight. For adults, a BMI of 25.0 to 29.9 is classified as overweight, while a BMI of 30.0 or higher is classified as obese. However, it's important to note that BMI does not directly measure body fat and can be less accurate in individuals with high muscle mass, such as athletes.
For children and adolescents, BMI is interpreted using age- and sex-specific percentiles. A child with a BMI between the 85th and 95th percentile is considered overweight, and a BMI at or above the 95th percentile is considered obese.
Comparison Table[edit]
[4]| Child/Adolescent BMI Range || 85th to <95th percentile || ≥ 95th percentile| Category | Overweight | Obesity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A condition of excess body fat. | A more severe form of excess body fat, considered a chronic disease.[2] |
| Adult BMI Range | [4]| ≥ 30.0 | |
| Health Risks | Increased risk of various health problems. | Significantly higher risk of developing chronic diseases. |
| [5]Associated Conditions | High blood pressure, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes. | Heart disease, stroke, certain cancers, sleep apnea, osteoarthritis. |
Causes and Contributing Factors[edit]
The fundamental cause of both overweight and obesity is an energy imbalance, where calorie intake surpasses energy expenditure. This imbalance[1] is influenced by a complex interplay of various factors.
Genetic predisposition can affect an individual's metabolism and how their body stores fat. Environmental factors also play a significant role. This includes easy access to high-calorie, processed foods and limited opportunities for physical activity, sometimes referred to as an "obesogenic environment". Lifestyle behaviors such as an unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, insufficient sleep, and high stress levels are major contributors. Certain medical conditions, like hypothyroidism, and some medications, including steroids and certain antidepressants, can also lead to weight gain.
Health Implications[edit]
Both overweight and obesity increase the risk of numerous health problems, with the risk escalating as BMI increases. Individuals who are overweight or obese are more susceptible to developing high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes.
Obesity is associated with a greater likelihood of more severe health complications. These include an elevated risk for heart disease, stroke, and several types of cancer. Other related conditions are gallbladder disease, osteoarthritis, sleep apnea, and breathing problems. Furthermore, obesity can negatively impact mental health, leading to issues like depression and anxiety, and can reduce overall quality of life by causing body pain and difficulties with physical functioning. In pregnant individuals, being overweight or obese can increase the risk of complications for both the mother and the child.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "who.int". Retrieved January 20, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "myjuniper.com". Retrieved January 20, 2026.
- ↑ "ubiehealth.com". Retrieved January 20, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "nih.gov". Retrieved January 20, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "laparoscopicsurgeons.com". Retrieved January 20, 2026.