Differences between Principal and Principle
Contents
Comparison Article[edit]
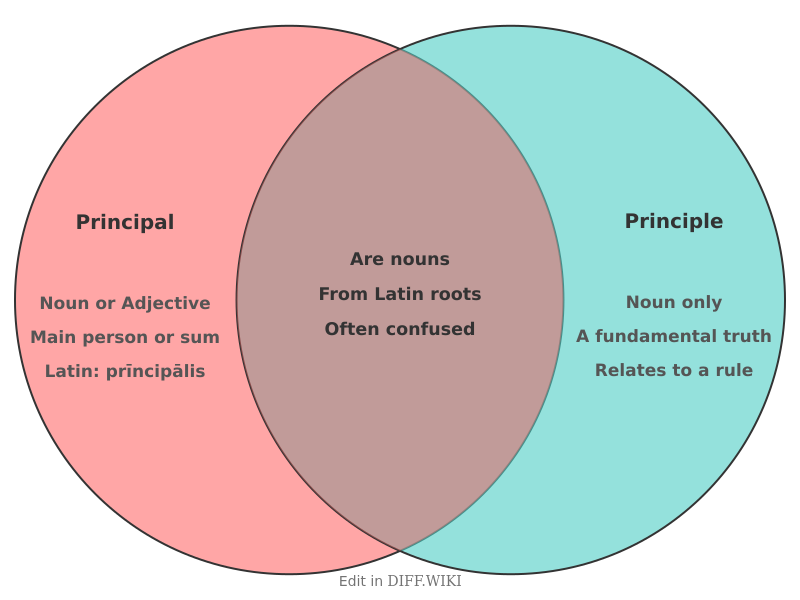
The homophones principal and principle are frequently confused in English.[1][2] Both words originate from the Latin prīmus, meaning "first". Despite[3] their similar roots and identical pronunciation, their meanings are distinct. [4]Principal can function as a noun or an adjective, while principle is only ever a noun. [5]
Comparison Table[edit]
[3]| Example (Person) || The school principal announced a snow day. || N[2]/A| Category | Principal | Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Part of Speech | Noun or Adjective | Noun only |
| Primary Meaning | Main, most important, or a person in a leading role [5][2] | A fundamental truth, rule, or belief |
| Etymology | From Latin prīncipālis ("first, chief") | [3] From Latin prīncipium ("beginning, origin") |
| Example (Finance) | The loan payments cover both principal and interest. | N/A |
| Example (Adjective) | The principal reason for the delay was traffic. | N/A |
| Example (Rule/Belief) | N/A | The company was founded on the principle of customer service. |
Usage of Principal[edit]
The word principal can be used as both a noun and an adjective.
As a noun, principal most commonly refers to a person who holds a high position of authority. This[5] is often the head of a school or educational institution. It can also denote a leading person in other contexts, such as the principal performer in an orchestra or a key figure in a business. In finance,[5] principal refers to the original sum of money invested or lent, separate from interest.
As an adjective, principal means "main" or "most important." It is[3][1] used to signify the primary or leading element among others. For example, one might refer to the "principal ingredient" in a recipe or the "principal cause" of an event.
[1]= Usage of Principle =[edit]
Principle is exclusively a noun and typically refers to a fundamental truth, law, or doctrine. It can describe a moral rule or a standard of good behavior. For instance, a person might refuse to do something "on principle" or be described as a "person of principle."
The term also applies to established scientific laws or the basic tenets of a system. Examples[1] include the "principles of physics" or the "principles of democracy." The phrase "in principle" is used to convey agreement with an idea in theory, though perhaps not in practice.
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "gingersoftware.com". Retrieved December 10, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "conturae.com". Retrieved December 10, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "dictionary.com". Retrieved December 10, 2025.
- ↑ "grammarly.com". Retrieved December 10, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "merriam-webster.com". Retrieved December 10, 2025.