Differences between Scuba Diving and Snorkeling
Contents
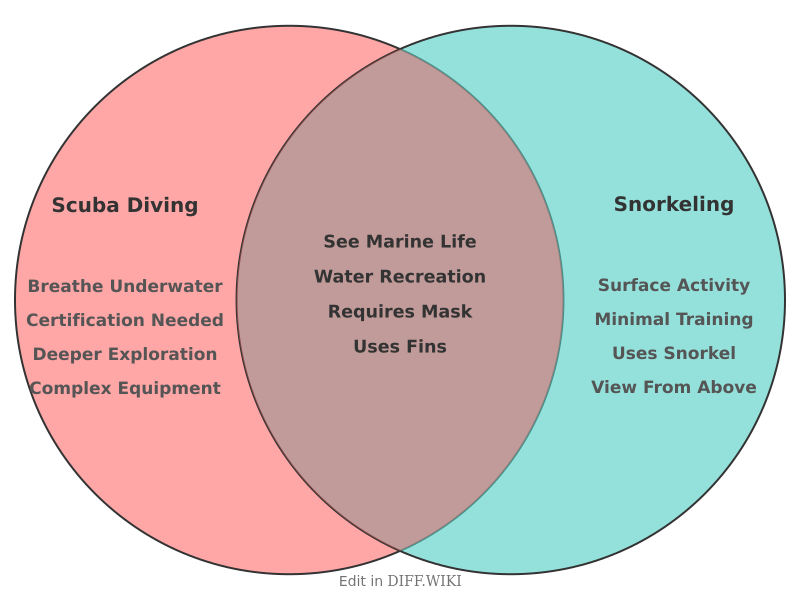
Scuba Diving vs. Snorkeling[edit]
Scuba diving and snorkeling are two methods of observing underwater environments. The primary distinction between them relates to the breathing apparatus used and the resultant depth of underwater exploration.[1][2] Snorkeling is the practice of swimming on or through a body of water while equipped with a diving mask, a shaped breathing tube called a snorkel, and usually swimfins. Scuba diving involves the use of a self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (scuba), which is completely independent of surface supply, to breathe underwater.[1]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Scuba Diving | Snorkeling |
|---|---|---|
| Breathing Method | Breathes compressed air from a tank via a regulator.[2][3] | Breathes surface air through a tube (snorkel).[2] |
| Typical Depth | Can explore depths from 18 meters (60 feet) for beginners to over 40 meters (130 feet) for advanced divers.[3] | Primarily a surface activity, with participants floating or making shallow dives of a few meters.[4][5] |
| Equipment | Requires extensive gear including a mask, fins, scuba tank, regulator, buoyancy control device (BCD), and weights.[1][5] | Requires minimal equipment: a mask, snorkel, and fins.[5] |
| Training and Certification | Requires formal training and certification from a recognized agency to ensure safety and proper equipment handling.[1] | Does not require certification; basic skills can be learned in a short amount of time. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to the cost of equipment, training, and guided dives. | More affordable, with lower equipment and entry costs. |
| Duration Underwater | Allows for extended periods underwater, limited by the amount of air in the tank, depth, and decompression limits. | Limited to the swimmer's comfort at the surface; dives are restricted by the need to hold one's breath.[5] |
| Health Considerations | Requires a good level of physical fitness and may require medical clearance for certain conditions such as heart or lung issues.[1] | Accessible to most people who can swim and are comfortable in the water. |
| Safety Risks | Inherent risks include decompression sickness, equipment malfunction, and barotrauma if safety procedures are not followed. | Generally considered lower risk, with primary concerns being sunburn, fatigue, and awareness of boat traffic. |
Skill Requirements[edit]
Snorkeling requires basic swimming ability and comfort in the water.[1] The techniques for clearing a snorkel of water and swimming with fins are typically learned quickly. Scuba diving necessitates a more comprehensive skill set acquired through certified training. This includes learning to control buoyancy, equalize pressure in the ears, read dive gauges, and handle potential emergencies underwater.[5]
Underwater Experience[edit]
Because snorkelers remain at or near the surface, they primarily observe marine life that inhabits shallower waters.[4] It offers a panoramic view from above.[1] Scuba diving allows for a more immersive experience, enabling participants to swim alongside marine creatures, explore shipwrecks, and see underwater geological formations at greater depths.[2][3] The ability to stay underwater for an extended time allows for more detailed and prolonged observation of the marine environment.[2]
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "adventures.com". Retrieved January 11, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "padi.com". Retrieved January 11, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "spiritliveaboards.com". Retrieved January 11, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "onbird.vn". Retrieved January 11, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 "dresseldivers.com". Retrieved January 11, 2026.