Differences between Transcription and Translation
Contents
Differences between Transcription and Translation[edit]
Transcription and translation are processes that convert information from one format to another. Though the terms are used in multiple fields, including linguistics and genetics, the core distinction remains consistent: transcription involves rendering information in the same language but a different medium, while translation involves converting information from a source language to a different target language.[1]
In linguistics and professional services, transcription is the process of converting spoken language into a written text.[2][3] For example, a court reporter transcribes spoken testimony into a written document.[2] Translation converts written text from one language into another, such as translating a novel from English into French. The key difference is the language; transcription stays within the original language, whereas translation crosses between two different languages.[4][1]
In genetics, the terms describe the two main stages of gene expression.[5] Transcription is the process where a segment of DNA is copied into a complementary strand of messenger RNA (mRNA).[5] This occurs within the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. Translation follows transcription; it is the process where the genetic code carried by mRNA is decoded by a ribosome to produce a specific sequence of amino acids, creating a protein.
Comparison Table[edit]
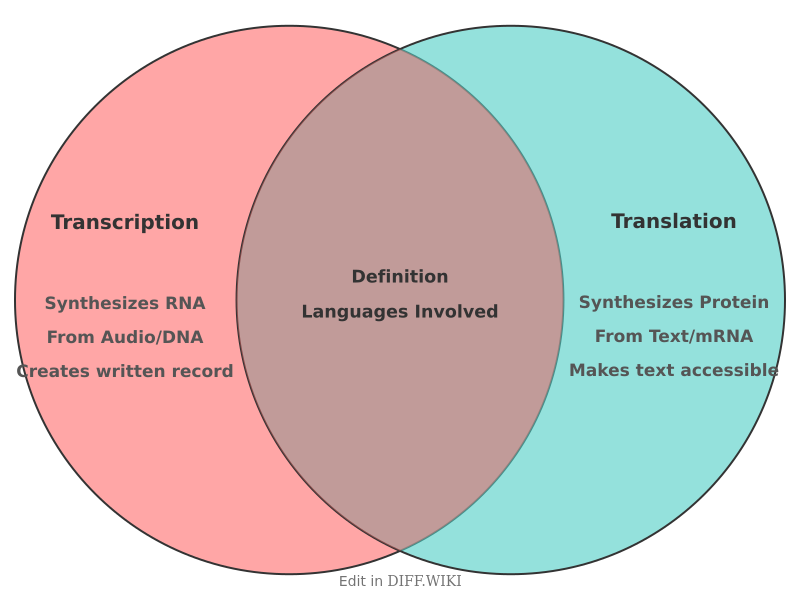
| Category | Transcription | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process of converting spoken language or genetic information into a written or complementary format within the same language.[2][3][5] | The process of converting the meaning of text or genetic code from a source language into a target language.[4][5] |
| Languages Involved | One. The language of the source and output is the same.[1] | Two or more. It converts content from a source language to a different target language.[1] |
| Medium | Converts from an audio or DNA source to a written text or RNA format.[5] | Typically converts a written text in one language to a written text in another.[4] |
| Linguistic Application | Creating a written record of an interview or court proceeding.[2] | Making a book or document accessible to speakers of another language. |
| Genetic Process | Synthesizing an RNA strand from a DNA template in the cell's nucleus (in eukaryotes).[5] | Synthesizing a protein from an mRNA template at the ribosome in the cytoplasm.[5] |
| Input/Precursor | Spoken audio or a DNA strand.[5] | Written text or an mRNA strand.[5] |
| Output/Product | A written document (e.g., a transcript) or an RNA molecule.[5] | A written document in a new language or a protein.[5] |
See also[edit]
- Transliteration
- Gene expression
- Central dogma of molecular biology
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "acutrans.com". Retrieved November 29, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved November 29, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "quora.com". Retrieved November 29, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved November 29, 2025.
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 "quora.com". Retrieved November 29, 2025.