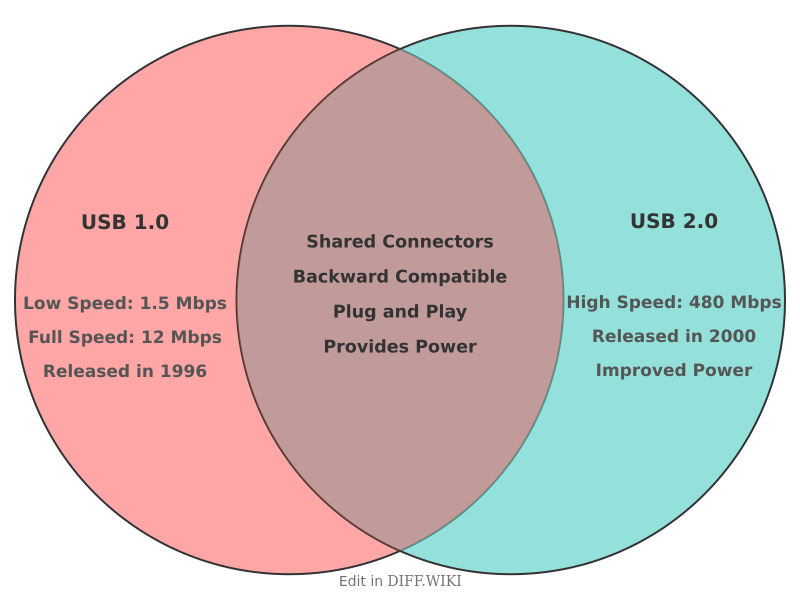
Differences between USB 1.0 and USB 2.0
USB 1.0 vs. USB 2.0[edit]
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that establishes specifications for cables, connectors, and protocols for connection, communication, and power supply between computers, peripherals, and other computers.[1] USB was developed to standardize the connection of peripherals to computers, replacing various interfaces like serial and parallel ports.[1] This article outlines the key differences between the first major version, USB 1.0, and its successor, USB 2.0.
USB 1.0 was released in January 1996.[1] It offered two data transfer speeds: 1.5 megabits per second (Mbps) at low speed and 12 Mbps at full speed.[2] A revised version, USB 1.1, was released in August 1998, matching the data rates of 1.0 but with improvements that led to wider adoption.[1][3]
USB 2.0, released in April 2000, introduced a significantly faster maximum signaling rate of 480 Mbps, branded as "High Speed".[1][4] This was a substantial increase, making it 40 times faster than the USB 1.1 "Full Speed" rate.[4] Despite the new maximum speed, USB 2.0 remained backward compatible, able to operate at the older 12 Mbps and 1.5 Mbps speeds for devices that required less bandwidth.[2]
In terms of power delivery, both USB 1.0 and 2.0 standard downstream ports were designed to provide up to 500 mA at 5 V, equating to a total power output of 2.5 watts.[5] While the base power specification remained the same, the release of the USB Battery Charging Specification after USB 2.0 allowed for devices to draw higher currents.
Another advancement with USB 2.0 was the introduction of USB On-The-Go (OTG), which allows two USB devices to communicate with each other without needing a separate USB host.[2] The USB 2.0 standard also supported a wider variety of connectors, including the Mini and Micro connectors that were introduced later to accommodate smaller devices.[2][3]
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | USB 1.0/1.1 | USB 2.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Release Date | January 1996 (1.0), August 1998 (1.1)[1] | April 2000[1] |
| Maximum Data Transfer Rate | 12 Mbps (Full Speed)[2] | 480 Mbps (High Speed)[1] |
| Other Supported Speeds | 1.5 Mbps (Low Speed)[2] | 12 Mbps, 1.5 Mbps[2] |
| Marketing Name | Full Speed (for 12 Mbps)[2] | High Speed[2] |
| Standard Power Output | 5V, up to 500mA (2.5W) | 5V, up to 500mA (2.5W) |
| Connector Types | Type A, Type B[2] | Type A, Type B, Mini A, Mini B, Micro A, Micro B[2] |
| USB On-The-Go (OTG) | Not supported | Supported[2] |
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved December 03, 2025.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 "sameskydevices.com". Retrieved December 03, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "usb-tec.com". Retrieved December 03, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "silverstonetek.com". Retrieved December 03, 2025.
- ↑ "cadence.com". Retrieved December 03, 2025.