Differences between Windows 8 and Windows RT
Windows 8 vs. Windows RT[edit]
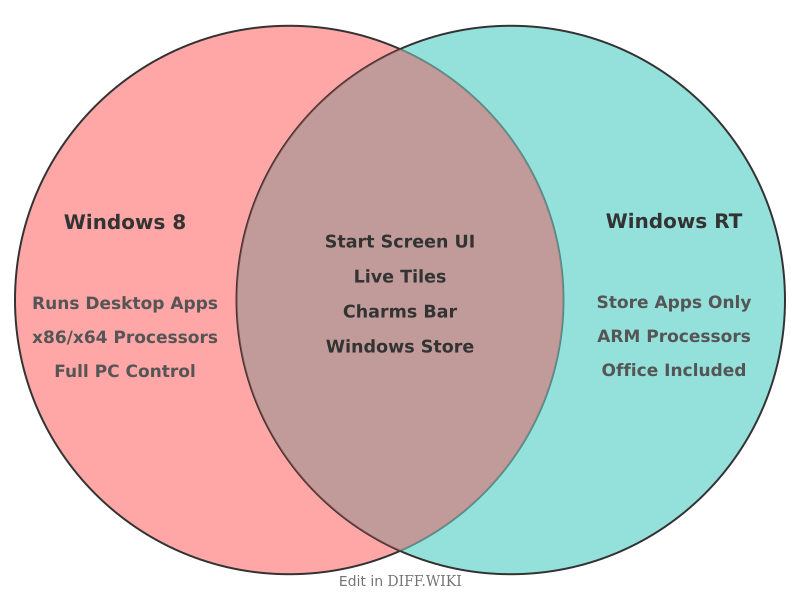
Windows 8 and Windows RT were two distinct operating systems released by Microsoft in 2012, sharing a similar user interface but differing fundamentally in their underlying architecture and capabilities.[1][2] Windows 8 was the primary version for traditional desktops, laptops, and tablets using x86-based processors from Intel and AMD.[3][4] In contrast, Windows RT was specifically designed for thinner, more power-efficient devices running on ARM-based processors.[5] This architectural divergence was the core reason for the significant differences in application compatibility and target hardware between the two operating systems.
The most critical distinction for users was software compatibility. Windows 8 could run both new applications from the Windows Store and traditional desktop programs that were compatible with previous versions of Windows. Windows RT, however, was a more restricted environment. It could not run legacy x86 desktop software. Users of Windows RT devices were limited to installing applications available through the Windows Store, along with a preinstalled version of Microsoft Office 2013 RT.[5] This limitation was a deliberate design choice to create a more controlled and secure user experience.[5]
Windows RT was only available pre-installed by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) on specific devices, such as the initial Microsoft Surface tablet.[3][2] It was not sold directly to consumers as a standalone software package.[3] Windows 8, however, was widely available on a vast range of devices from various manufacturers and could also be purchased separately for installation on compatible PCs.[4] The hardware for Windows RT was generally less powerful but offered longer battery life, positioning it against other mobile operating systems.[1]
Ultimately, the limitations on software, particularly the inability to run familiar desktop applications, led to the discontinuation of Windows RT devices.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Windows 8 | Windows RT |
|---|---|---|
| Processor Architecture | x86 (Intel, AMD)[4] | ARM[5] |
| Desktop App Compatibility | Full support for traditional Windows (x86) applications | No support for traditional Windows (x86) applications |
| Application Installation | Windows Store and third-party desktop applications | Primarily Windows Store only |
| Included Office Suite | Not included, purchased separately[4] | Microsoft Office Home & Student 2013 RT pre-installed[5] |
| Target Hardware | Desktops, laptops, and tablets[4][2] | Thin and light tablets and convertible devices[1][5] |
| Availability | Sold pre-installed on new devices and as a separate retail product[3][4] | Only available pre-installed on specific OEM devices[3] |
| Windows Media Player | Included[4] | Not included; replaced by Xbox Music and Video apps[5] |
| Domain Join | Supported in Pro and Enterprise editions | Not supported |
See also[edit]
- Windows 8 editions
- Microsoft Surface
References[edit]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "informationweek.com". Retrieved December 28, 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "r-tt.com". Retrieved December 28, 2025.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "superuser.com". Retrieved December 28, 2025.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 "techradar.com". Retrieved December 28, 2025.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 "wikipedia.org". Retrieved December 28, 2025.