Differences between Xanax- and Klonopin
Contents
Comparison Article[edit]
I have gathered information on the primary uses, drug class, mechanism of action, onset of action, duration of effects, and half-life for both Xanax (alprazolam) and Klonopin (clonazepam). The search results provide sufficient detail to create a comprehensive comparison, including a table of key differences, and to write a 500-word article in the requested format. I can now proceed with generating the Wikipedia-formatted article.
Xanax vs. Klonopin[edit]
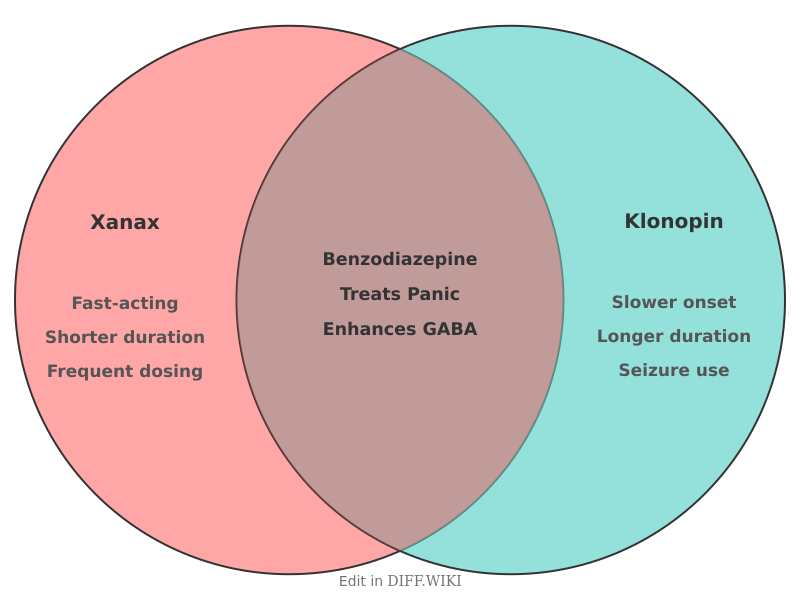
Xanax, the brand name for alprazolam, and Klonopin, the brand name for clonazepam, are both prescription medications classified as benzodiazepines.[1] These drugs act on the central nervous system to produce a calming effect.[2][3] Both are frequently prescribed for anxiety and panic disorders, but they have distinct differences in their approved uses, duration of action, and how quickly they work.[4][5]
Both Xanax and Klonopin enhance the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain.[2] GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning it reduces the activity of nerve cells, which leads to the sedative, anti-anxiety, and muscle-relaxant properties of these medications.[2][3] Although they share a common mechanism of action, their pharmacokinetic profiles—how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and excretes the drugs—differ significantly, leading to variations in their clinical use.
Comparison Table[edit]
| Category | Xanax (Alprazolam) | Klonopin (Clonazepam) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary FDA-Approved Uses | Anxiety disorders, panic disorder | Seizure disorders, panic disorder |
| Drug Class | Benzodiazepine | Benzodiazepine |
| Mechanism of Action | Enhances the effect of GABA at the GABA-A receptor | Enhances[2] the effect of GABA at the GABA-A receptor |
| Onset of Action | Fast-acting, with effects felt within an hour | Slower onset, with effects beginning within one hour |
| Peak Plasma Concentration | 1 to 2 hours | 1 to 4 hours |
| Duration of Effects | Shorter-acting, effects last 4 to 6 hours | Longer-acting, effects last up to 12 hours or more |
| Elimination Half-Life | About 11.2 hours in healthy adults | 30 to 40 hours |
| Dosing Frequency | Typically taken three times a day | Typically[4] taken once or twice daily |
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
The primary difference between Xanax and Klonopin lies in how long they remain in the body. Xanax is absorbed and reaches peak concentrations in the blood relatively quickly, within 1 to 2 hours. Its effects are also shorter-lived, generally lasting between 4 and 6 hours. This makes it suitable for the immediate relief of acute anxiety or panic attacks. Because[5] of its shorter duration, it often requires more frequent dosing, typically three times per day.
In[4] contrast, Klonopin has a longer duration of action, with therapeutic effects that can last for 12 hours or more. It reaches peak blood concentrations more slowly, typically within 1 to 4 hours after administration. Klonopin's extended-release profile allows for less frequent dosing, often once or twice daily, which can be beneficial for providing consistent, all-day relief from symptoms. The[5] elimination half-life of Klonopin is significantly longer than that of Xanax, ranging from 30 to 40 hours, compared to approximately 11.2 hours for Xanax.
Clinical Applications[edit]
Due to its rapid onset and short duration, Xanax is primarily indicated for the management of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and the acute treatment of panic attacks. Klonopin is also approved for treating panic disorder. However, a key difference in their approved uses is that Klonopin is also an anticonvulsant medication used to manage certain types of seizure disorders in both adults and children, an indication for which Xanax is not used.
Both[4] medications carry a risk of dependence, withdrawal symptoms, and potential for misuse. Due[5] to its faster onset of action, Xanax may have a higher potential for addiction for some individuals. Discontinuation[5] of either medication should be done under medical supervision to minimize withdrawal effects.[5]
References[edit]
- ↑ "therecoveryvillage.com". Retrieved January 28, 2026.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "benzoinfo.com". Retrieved January 28, 2026.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "homehealthpatienteducation.com". Retrieved January 28, 2026.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "goodrx.com". Retrieved January 28, 2026.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 "medvidi.com". Retrieved January 28, 2026.