Difference between revisions of "Difference between Mexican and Spanish Food"
(Created page with "thumb|left|Paella is most likely the most popular Spanish dish File:Tai-s-captures-JiRSy0GfqPA-unsplash.jpg|thumb|right|Mexic...") |
m (Reverted edits by Admin (talk) to last revision by 178.197.229.7) Tag: Rollback |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
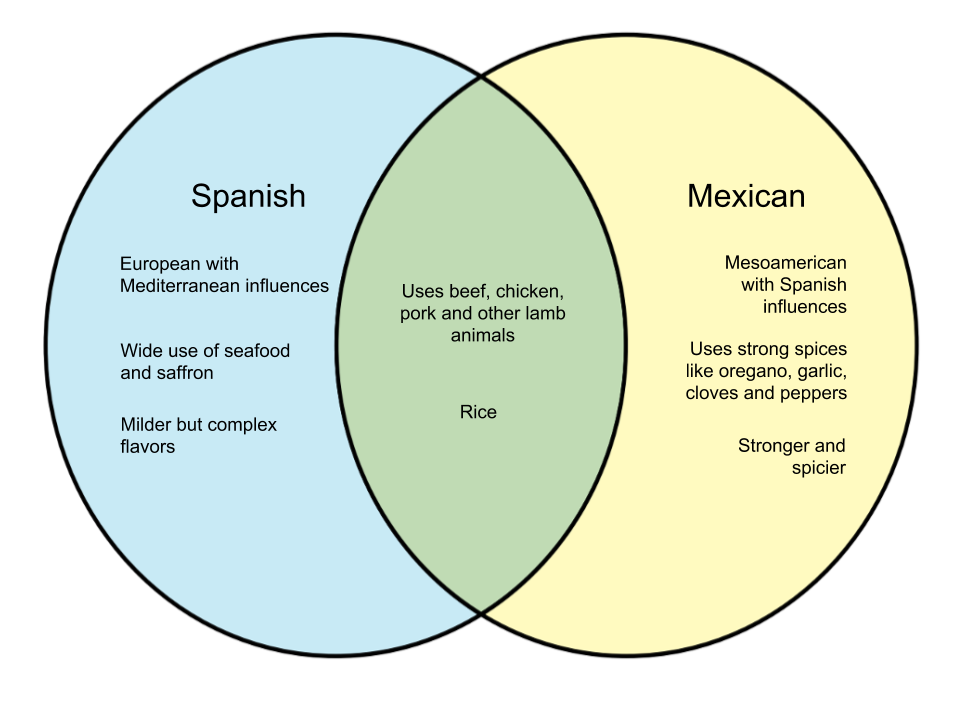
=== Venn Diagram === | === Venn Diagram === | ||
[[File:Difference-Between-Spanish-and-Mexican-Food.png|center]] | [[File:Difference-Between-Spanish-and-Mexican-Food.png|center]] | ||
| + | Land* | ||
Latest revision as of 23:20, 26 March 2021
Spanish and Mexican cultures are so closely related that we often confuse one thing for the other. This also includes their cuisine, which at a glance may almost seem like they came from the same place. In this article, we will highlight the differences between Spanish and Mexican food.
Spanish cuisine has its roots from European cuisine, sporting a Mediterranean style that makes use of seafood in many dishes. The wide use of seafood as well as the Middle Eastern influence is one of the biggest distinguishing factors between Spanish and Mexican food. Spanish food is considerably milder, employing less use of spices and relying more on complexity of flavor. Saffron is also a widely used ingredient.
Spanish cuisine is also influenced by the different cultures that had passed through over the generations, such as the Arabs, Persians, Romans and Indians. Another thing worth noting is the preparation of tortillas. Whereas Spanish tortillas are made with eggs like an omelette, tortillas in Mexico use corn flour and are in the form of flatbread.
Mexican cuisine is influenced by Spanish culture, but is also mainly based on Mesoamerican cooking. It does not use as much seafood but relies on land meat like chicken, pork, and beef. There is a wider array of spices in Mexican cooking and their dishes are generally stronger and spicier than Spanish food.
| Spanish cuisine | Mexican food | |
|---|---|---|
| Origin and influences | European cuisine, with Mediterranean influences; Influence from Arabs, Romans, Persians and Indians | Mesoamerican cuisine with Spanish influences |
| Staples | Fish, mussels, seafood, land meats, vegetables, olive oil | Land meats, rice, corn, corn flour, beans |
| Spices | A bit of spices, mostly saffron | Peppers, cilantro, oregano, garlic, cloves and other strong spices |
| Flavor | Milder than Mexican food, reliant on complex flavors | Strong and spicy |
| Desserts | Mostly rice-based | Mostly flour-based |
| Tortillas | Uses eggs like an omelette | Uses corn flour and has the characteristics of flatbread |
| Examples | Paella, gazpacho, chorizo, pisto | Burritos, quesadillas, tacos, enchiladas, salsa |
Venn Diagram[edit]
Land*