Difference Between Cannabinoids and THC
As considerations on the legalization of marijuana has become more widespread, so does the information about their advantages. Cannabinoids and THC are marijuana-related terms that are taken into consideration when it comes to research, development, and application. In this article, we will feature the differences between cannabinoids and THC.
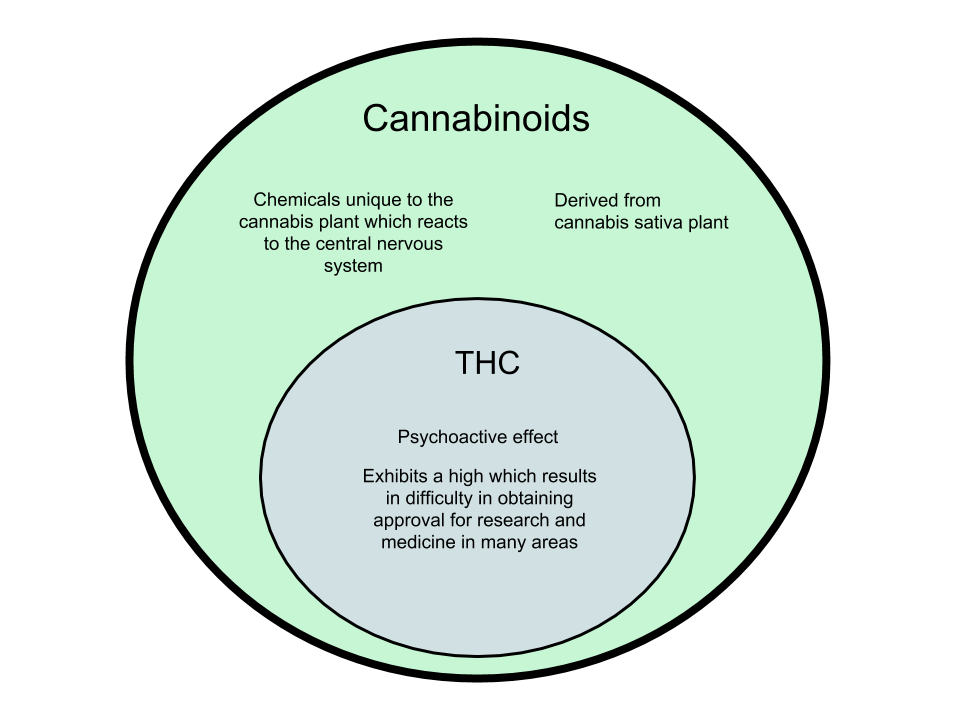
The Cannabis sativa is composed of over 480 components, 66 of them being classified as cannabinoids. These are chemicals that are unique to the plant, reacting to various receptors in the human body when cannabis is interacted with. These receptors can be found in the central nervous system and are divided into two types - CB1 and CB2. There are different classes of cannabinoids like CBD, THC, CBN, and CBDL.
THC is also known as tetrahydrocannabinol. THC is very similar to CBD and are even considered as “sister molecules.” THC is a psychoactive type of cannabinoid and induces a ‘high’ effect. Because of this, it is not as accepted for medicinal uses compared to the other types.
| Header text | Cannabinoids | THC |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chemicals unique to the cannabis plant which reacts to the central nervous system when applied by a user | A type of cannabinoid that is known for its psychoactive effect |
| Source | Cannabis sativa plant | Cannabis sativa plant |
| Also called | N/A | Tetrahydrocannabinol |
| Does it produce a high? | Depends on the type | Yes |
| Benefits | Depending on the type; examples are reduction of pain and inflammation, decreased anxiety, and stimulation of the appetite | Pain relief, increase in appetite, treatment of insomnia and glaucoma |
| Side Effects | Depends on the type and interactions with other drugs | Increased heart rate, red eyes, memory loss, delayed reaction time, issues with coordination |
| Applications | Depends on the type; examples are gels, oils, and supplements | Smoking marijuana, edibles, capsules, oils, and many more |
| Molecular Formula | Depends on the type | C21H30O2 |
| Molecular Mass | Depends on the type | 314.464 g/mol |
| Legality in the US. | Depends on the type; over 20 states have made medical marijuana legal; prone to changes | Controlled substance; 9 states have made recreational marijuana and THC legal; still prone to changes |